Overhead Absorption Steps, Methods, Calculation, Application

Manufacturing overheads are indirect costs which cannot be directly attributed to individual product units and for this reason need to be applied to the cost of a product using a predetermined overhead rate. In order to find the overhead rate we will use the same basis that we have chosen by multiplying this basis by the calculated how to calculate pohr rate. For example, if we choose the labor hours to be the basis then we will multiply the rate by the direct labor hours in each task during the manufacturing process. This is related to an activity rate which is a similar calculation used in Activity-based costing. A pre-determined overhead rate is normally the term when using a single, plant-wide base to calculate and apply overhead. Overhead is then applied by multiplying the pre-determined overhead rate by the actual driver units.
Problems with Predetermined Overhead Rates
- Our work has been directly cited by organizations including Entrepreneur, Business Insider, Investopedia, Forbes, CNBC, and many others.
- For example, we can use labor hours worked, and for calculating overhead for the store department, we can use the quantity of material to be used.
- The overhead rate has limitations when applying it to companies that have few overhead costs or when their costs are mostly tied to production.
- Further, it is stated that the reason for the same is that overhead is based on estimations and not the actuals.
- As you can see, calculating your predetermined overhead rate is a crucial first step in pricing your products correctly.
If the actual overhead at the end of the accounting period is 1,575 the overhead is said to be under applied by 125 (1,450 – 1,575). If the actual overhead at the end of the accounting period is 1,575 the overhead is said to be over applied by 25 (1,600 – 1,575). cash flow The overhead will be allocated to the product units at the rate of 10.00 for each machine hour used. Again the actual overhead at the end of the accounting period is 1,575 and the overhead is said to be under applied by 81 (1,494 – 1,575) as shown below.
Percentage of Direct Labor Cost

For example, let’s say the marketing agency quotes a client $1,000 for a project that will take 10 hours of work. The agency knows from its predetermined overhead rate that it will incur $200 in overhead costs for the project. This means that for every dollar of direct labor costs, the business will incur $0.20 in overhead costs.
Formula to Calculate Predetermined Overhead Rate

For instance, if the activity base is machine hours, you calculate predetermined overhead rate by dividing the overhead costs by the estimated number of machine hours. This is calculated at the start of the accounting period and applied to production to facilitate determining a standard cost for a product. Commonly used allocation bases are direct labor hours, direct labor dollars, machine hours, and direct materials cost incurred by the process. If an actual rate is computed monthly or quarterly, seasonal factors in overhead costs or in the activity base can produce fluctuations in the overhead rate. For example, the costs of heating and cooling a factory in Illinois will be highest in the winter and summer months and lowest in the spring and fall.
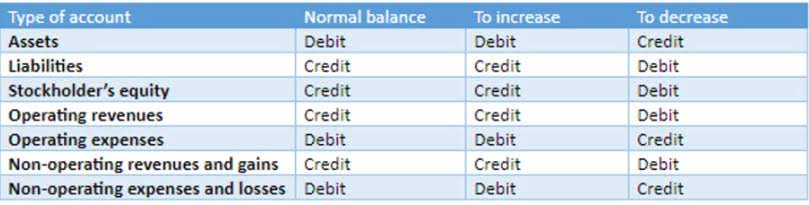
- The comparison of applied and actual overhead gives us the amount of over or under-applied overhead during the period which is eliminated through recording appropriate journal entries at the end of the period.
- Company B wants a predetermined rate for a new product that it will be launching soon.
- He has been a manager and an auditor with Deloitte, a big 4 accountancy firm, and holds a degree from Loughborough University.
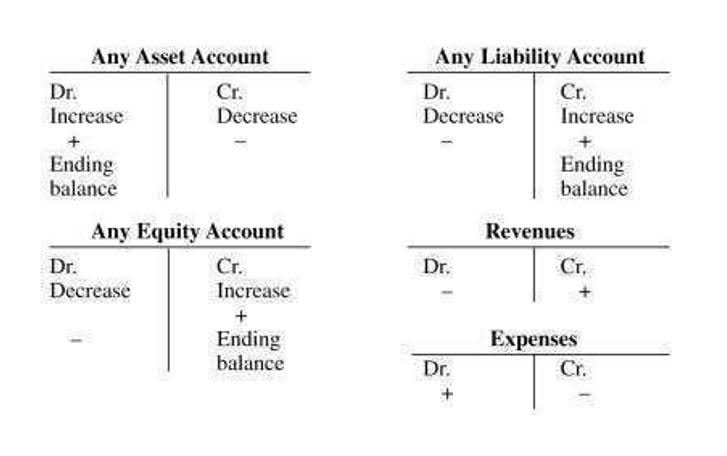
- We know that both direct materials and direct labor determine the nature of overheads.
- Any difference between applied overhead and the amount of overhead actually incurred is called over- or under-applied overhead.
- Suppose a business uses direct labor hours as the activity base for calculating the pre-determined rate.
This comparison can be used to monitor or predict expenses for the next project (or fiscal year). Using the predetermined overhead rate formula and calculation provides businesses with a percentage they can monitor on a quarterly, monthly, or even weekly basis. Businesses monitor relative expenses by having an idea of the amount of base and expense that is being proportionate to each other. This can help to keep costs in check and to know when to cut back on spending in order to stay on budget. The predetermined overhead rate formula can be used to balance expenses with production costs and sales. For businesses in manufacturing, establishing and monitoring an overhead rate can help keep expenses proportional to production volumes and sales.
- Each one of these is also known as an «activity driver» or «allocation measure.»
- He has worked as an accountant and consultant for more than 25 years and has built financial models for all types of industries.
- You can determine the direct labor involved by measuring how long it takes workers to provide a service or to make a product.
- Costs must thus be estimated based on an overhead rate for each cost driver or activity.
- The most prominent concern of this rate is that it is not realistic being that it is based on estimates.
- Therefore, the single rate overhead recovery rate is considered inappropriate, but sometimes it can give maximum correct results.

This can result in abnormal losses as well and unexpected expenses being incurred. Obotu has 2+years of professional experience in the business and finance sector. Her expertise lies in marketing, economics, finance, biology, and literature.

The company has direct labor expenses totaling $5 million for the same period. The equation for the overhead rate is overhead (or indirect) costs divided by direct costs or whatever you’re measuring. Direct costs typically are direct labor, direct machine costs, or direct material costs—all expressed in dollar amounts. Each one of these is also known as an «activity driver» or «allocation measure.» virtual accountant The use of such a rate enables an enterprise to determine the approximate total cost of each job when completed. In recent years increased automation in manufacturing operations has resulted in a trend towards machine hours as the activity base in the calculation.